
Freeze-dried agarose gels: A cheap, simpe and recyclable adsorbent for the purification of methylene blue from industrial wastewater
W.Y. Seow and C.A.E. Hauser
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 4 (2016) 1714-1721
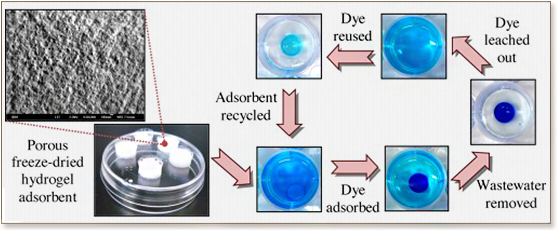
Dye colourants are being produced yearly on the kilotonne-scale and a significant percentage end up as highly-polluting industrial effluents. Freeze-dried agarose gels are demonstrated here to be efficient adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue, an important industrial dye. A hydrogel adsorbent offers advantages over powdered formulations, which can be difficult to handle. Freeze-drying further allows the adsorbent to be packaged, transported and stored in a dry format, thus conferring cost savings. Parameters such as the volume or concentration of agarose or dye, exposure time, pH and gel/water contact area influenced adsorption capacity and kinetics. Salt inhibited adsorption in a dose-dependent manner and this was exploited for the recycling of adsorbent and dye. Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms were also applied to model the adsorption process. The freeze-dried agarose gel achieved an adsorption capacity of 10.4 ± 0.2 mg/g, which was comparable to commercial activated carbon assessed under similar conditions. Additionally, unlike most activated carbon, agarose is derived from a renewable source. Since agarose is cheaply available commercially, this method can enjoy rapid industrial translation.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.02.013

"KAUST shall be a beacon for peace, hope and reconciliation, and shall serve the people of the Kingdom and the world."
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, 1924 – 2015
Thuwal 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Al-Haytham Building (Bldg. 2)
© King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. All rights reserved