
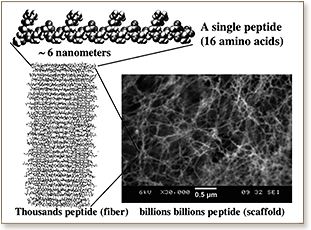
Cell and tissue engineering therapies for regenerative medicine as well as cell-based assays require an understanding of the interactions between cells with the surrounding microenvironment at the nanoscale. Engineering a cell-interactive scaffold therefore entails control over the nanostructure of the biomaterial. Peptides that are able to self-assemble into 3D scaffolds have emerged as interesting biomaterials for directing cell behavior, with desirable properties such as the capability of tuning the nanostructure by modulating the amino acid composition. Here, an overview of the development of self-assembling peptide hydrogels as functional cell scaffolds is presented, highlighting recent work on incorporating features such as bioactive ligands, growth factor delivery, controlled degradation, and formulation into microgels for defined cell microenvironments.
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201101905

"KAUST shall be a beacon for peace, hope and reconciliation, and shall serve the people of the Kingdom and the world."
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, 1924 – 2015
Thuwal 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Al-Haytham Building (Bldg. 2)
© King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. All rights reserved