
Ultrasmall peptides self-assemble into diverse nanostructures: morphological evaluation and potential implications
A. Lakshmanan and C.A.E. Hauser
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12 (2011) 5736-5746
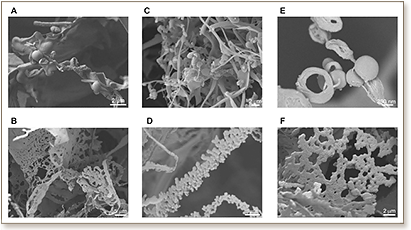
In this study, we perform a morphological evaluation of the diverse nanostructures formed by varying concentration and amino acid sequence of a unique class of ultrasmall self-assembling peptides. We modified these peptides by replacing the aliphatic amino acid at the C-aliphatic terminus with different aromatic amino acids. We tracked the effect of introducing aromatic residues on self-assembly and morphology of resulting nanostructures. Whereas aliphatic peptides formed long, helical fibers that entangle into meshes and entrap >99.9% water, the modified peptides contrastingly formed short, straight fibers with a flat morphology. No helical fibers were observed for the modified peptides. For the aliphatic peptides at low concentrations, different supramolecular assemblies such as hollow nanospheres and membrane blebs were found. Since the ultrasmall peptides are made of simple, aliphatic amino acids, considered to have existed in the primordial soup, study of these supramolecular assemblies could be relevant to understanding chemical evolution leading to the origin of life on Earth. In particular, we propose a variety of potential applications in bioengineering and nanotechnology for the diverse self-assembled nanostructures.
DOI: 10.3390/ijms12095736

"KAUST shall be a beacon for peace, hope and reconciliation, and shall serve the people of the Kingdom and the world."
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz Al Saud, 1924 – 2015
Thuwal 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Al-Haytham Building (Bldg. 2)
© King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. All rights reserved